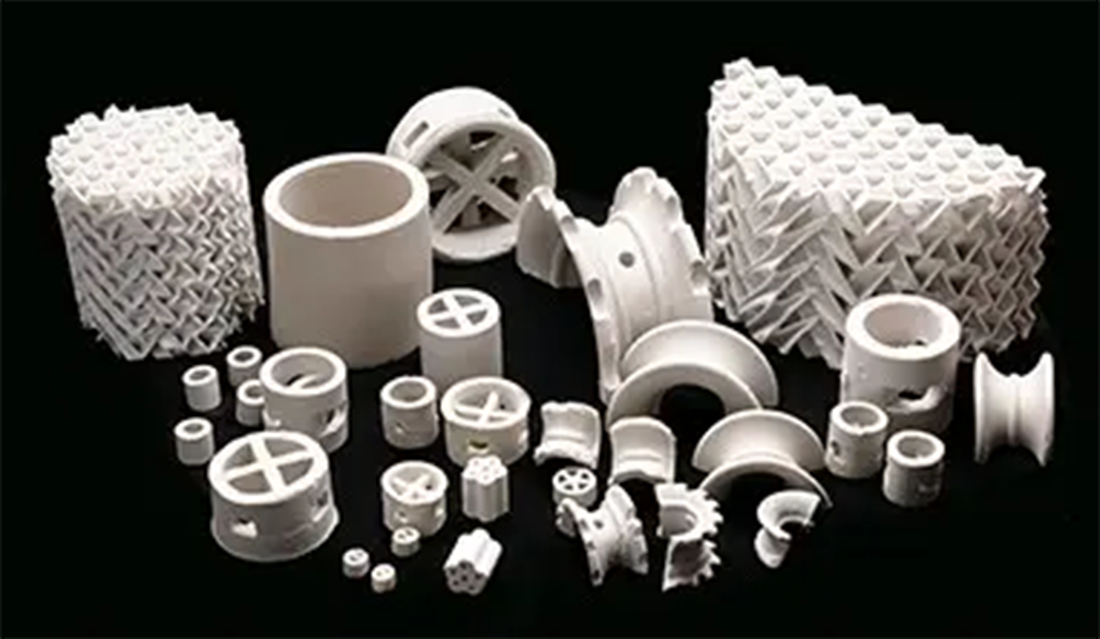
Ceramic random packing materials are particle-shaped packings made of ceramics, featuring high temperature resistance, resistance to acid and alkali corrosion, and strong chemical stability. They are widely used in fields such as chemical engineering, environmental protection, and petroleum. There are various types, including Raschig rings, pall rings, stepped rings, and rectangular saddle rings.

Raschig rings have a simple structure and low cost, making them suitable for traditional processes;
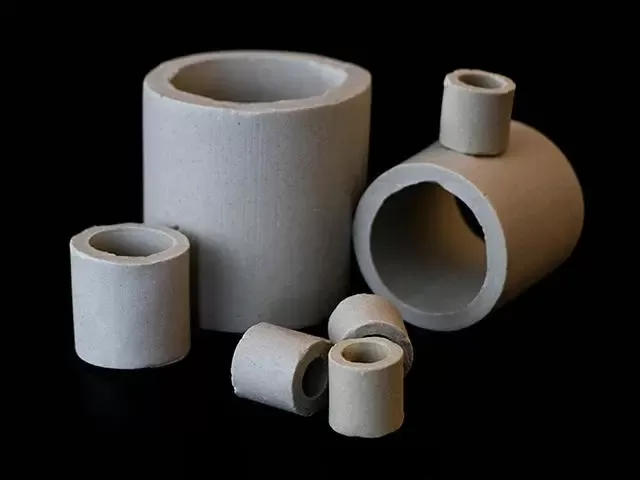

pall rings are improved versions based on Raschig rings, with higher mass transfer efficiency;

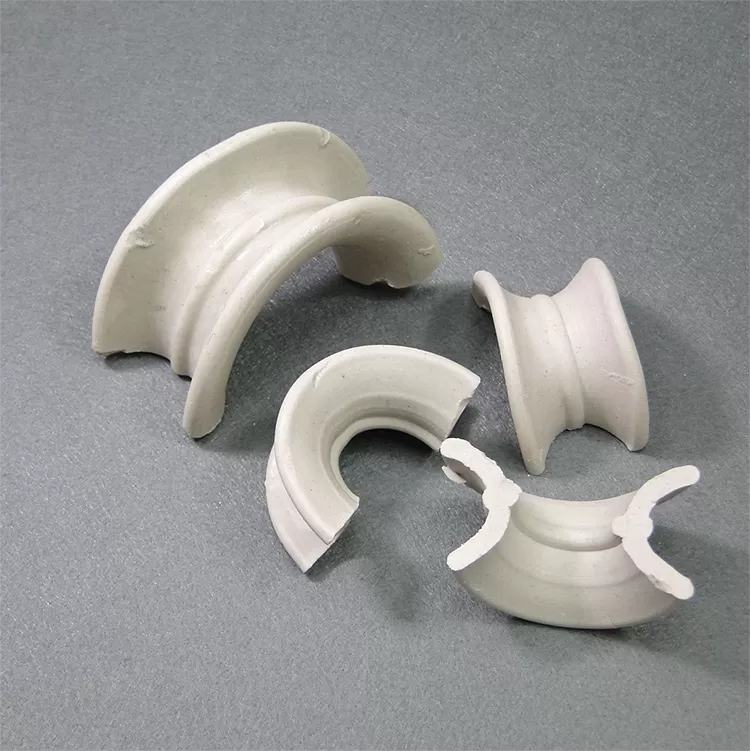
stepped rings have an asymmetrical design to reduce channel flow and have lower resistance;
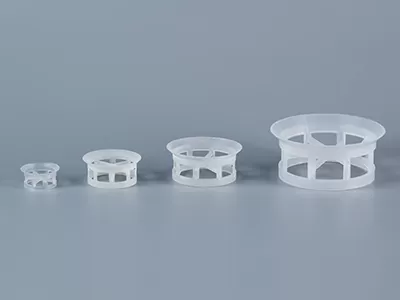
rectangular saddle rings have a saddle-shaped structure to increase surface utilization and provide more uniform fluid distribution.
After being piled up, these packings form voids, providing a surface for gas-liquid contact. Different types can be selected according to the working conditions to meet the requirements of separation and absorption processes, and they perform stably in harsh environments such as high temperatures and corrosive conditions.


.jpg)

.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)